EIGHT GRADE > 8.G.2 > TEACHER GUIDE
TEACHER GUIDE TO CLARIFICATION

8.G.2
Understand congruence and similarity using physical models, transparencies, or geometry software.
8.G.2 Understand that a two-dimensional figure is congruent to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations; given two congruent figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the congruence between them.
Verifying Experimentally Properties of Transformations


This is the traditional procedure of teaching transformations with ONE addition…SEQUENCED transformations to obtain the same results; with a focus on efficiency.
Comparing:
Graphs
Tables
Equations

Transformational geometry is about the effects of rigid motions, rotations, reflections and translations on figures. Initial work should be presented in such a way that students understand the concept of each type of transformation and the effects that each transformation has on an object before working within the coordinate system. For example, when reflecting over a line, each vertex is the same distance from the line as its corresponding vertex. This is easier to visualize when not using regular figures. Time should be allowed for students to cut out and trace the figures for each step in a series of transformations. Discussion should include the description of the relationship between the original figure and its image(s) in regards to their corresponding parts (length of sides and measure of angles) and the description of the movement, including the attributes of transformations (line of symmetry, distance to be moved, center of rotation, angle of rotation and the amount of dilation).The case of distance – preserving transformation leads to 8.G.3 where students are asked to use the coordinate plane to exercise the rigid motions.
An introductory activity might be creating each of the transformations in art to describe, practice and discuss each of the rigid motions. Here is an example:


These designs were created by 8th graders in East Richland school district. The “snowflake” design is a rotation of 60 or 90 degrees.
The reflection is the positive and negative image on construction paper and the long strips or friezes depict
translations. It is a good way to introduce the ideas and vocabulary.

This standard is the students’ introduction to congruency. Congruent figures have the same shape and size. Translations, reflections and rotations are examples of rigid transformations. A rigid transformation is one in which the pre-image and the image both have exactly the same size and shape since the measures of the corresponding angles and corresponding line segments remain equal (are congruent). Students examine two figures to determine congruency by identifying the rigid transformation(s) that produced the figures. Students recognize the symbol for congruency (≅) and write statements of congruency.
Examples:
-
Is Figure A congruent to Figure A‘? Explain how you know

-
Describe the sequence of transformations that results in the transformation of Figure A to Figure A‘
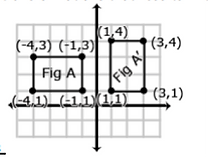
Student should discuss these questions and others about the transformation’s effects on the polygon and its sides and angles.
I'm a paragraph. Click here to add your own text and edit me. I’m a great place for you to tell a story and let your users know a little more about you.
Understandings should include generalizations about the changes that maintain size or maintain shape.
Students should be asked to describe the transformations required to go from an original figure to a transformed figure (image). Provide opportunities for students to discuss the procedure used, whether different procedures can obtain the same results, and if there is a more efficient procedure to obtain the same results. (see diagram A below) Students need to learn to describe transformations with both words and numbers.
Kansas Association of Teachers of Mathematics (KATM) Flipbooks. Questions or to send feedback: melisa@ksu.edu.
Retrieved from Math Flipbooks.
Figure A

Notice that in the diagram on the left, that it could be identified as a reflection over the x-axis; however, it can also be identified as a 180º clockwise rotation about the origin.
Students need to be exposed to images that can be created in more than one way.
Likewise, students need to consider whether the image which is created by a series of transformations can be achieved if the series of transformations is reversed.
Appropriate vocabulary is required….flip, turn, and slide are third grade terminology and have no place in 8th grade.
PARRC practice examples:
http://parcc.pearson.com/practice-tests/math/

13. Part A
Which statement describes a possible sequence of transformations that transforms figure 1 into figure 2?
A. a reflection across the x-axis, followed by a translation 2 units to the left.
B. a reflection across the x-axis, followed by a translation 3 units to the right.
C. a rotation 180 degrees clockwise about the origin followed by a translation 2 units to the left.
D. a rotation 180 degrees clockwise about the origin followed by a translation 3 units to the right.
Part B
Figure 3 can also be created by transforming figure 1 with a sequence of two transformations.
Which statement describes a possible sequence of transformations that transforms figure 1 into figure 3?
A. a rotation 180 degrees clockwise about the origin, followed by a translation 2 units to the left.
B. a rotation 90 degrees clockwise about the origin, followed by a reflection across the x-axis.
C. a rotation 180 degrees clockwise about the origin, followed by a reflection across the y-axis.
D. a rotation 90 degrees clockwise about the origin, followed by a translation 3 units to the right.
Rotate BAT where B(-5,3), A(-1,4), and T(-2,2) clockwise about the origin.
B’(____,___)
A’(____,___)
T’(____,___)
a. Describe how you did the rotation.
b. Describe what happened to the coordinates of each point:
Engage New York Module 2 End of Module Assessment Question 1
https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-8-mathematics-module-2
Use the picture to answer the statement below

Describe a sequence of rigid motions that would prove a congruence between and

Students should investigate problems where the image can be created from more than one sequence of transformations.
Coherence and Connections: Need to Know
Grade Below
Grade Level
Grade Above
7.G.2
7.G.5
8.G.1
8.G.2
8.G.4
8.G.5
G.CO
Students use prior knowledge from sixth and seventh grade related to measurement (congruency). In addition, the work in seventh grade surrounding angle types, i.e. vertical angles, corresponding angles, parallel lines crossed by a transversal, will serve as an anchor to pin the new concepts of congruency and symmetry.
Illinois Assessment of Readiness Evidence Tables: https://www.isbe.net/Documents/IAR-Grade-8-Math-Evidence-State.pdf
Evidence
Statement Key
Evidence Statement Text
Clarifications
MP
8.G.2
Understand that a two-dimensional figure is congruent to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations; given two congruent figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the congruence between them.
i) Tasks do not have a context. ii) Figures may be drawn in the coordinate plane, but do not include the use of coordinates.
iii) Tasks require students to make connections between congruence and transformations.
2,7
Calculator
No
8.C.3.2
Construct, autonomously, chains of reasoning that will justify or refute propositions or conjectures.
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 8.G.2, 8.G.4
3,5,6
Yes
8.C.5.2
Apply geometric reasoning in a coordinate setting, and/or use coordinates to draw geometric conclusions.
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 8.G.2, 8.G.4
Yes
2,3,5
Also check out Student Achievement Partners Coherence Map.
Classroom Resources
Short Mars Tasks
http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download.php?fileid=1189
HOT Questions
1. Translate ALT if A(-5,-1), L(-3,-2), T(-3,2). by the rule (x ,y) à(x + 6, y – 3 ), then reflect the image over the y-axis. Compare side lengths and angle measures of the two images. What did you find? (The notation used in the above
problem is NOT required. Students will not see this on PARCC)
Answer:
Side lengths and angle measures are congruent.
2. Perform the transformation: 180 degrees rotation about the origin, then do the following:
a. Write the new coordinates.
H'(3,3), F'(15), U'(4,5)
b. Find the area of the pre-image.
3 square units.
c. Find the area of the rotated image.
d. 3 square units.
e. Are they equal? Yes.
3. Use the image in Number 2 to answer the following questions.
-
Is area affected by translation or reflection? Explain. No congruency is maintained therefore area must be maintained.
-
Is perimeter affected by translation or reflection? Explain. No congruency is maintained therefore the perimeter is congruent.
4. (from Inside Mathematics)
https://www.insidemathematics.org/sites/default/files/materials/miles%20of%20tiles_44.pdf
Need to utilize systems to do this problem and tiles are the same even though the image does not look like it.

Answer:
The two equations are 2l + 2w = 8 and l =
Length is 2.5 ft and width is 1.5 ft.
Additional Resources
Illustrative Mathematics
http://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/8/G/A/2/tasks/646
http://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/8/G/A/2/tasks/903
http://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/8/G/A/2/tasks/1228
http://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/8/G/A/2/tasks/1230
http://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/8/G/A/2/tasks/1231
http://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/8/G/A/2/tasks/1232
Card Sort (Mars Task)
http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?taskid=490#task490
Inside Mathematics - Problem of the Month (Level D)
https://www.insidemathematics.org/sites/default/files/materials/between%20the%20lines_47.pdf
National Library of virtual manipulatives has 3 applets that can be used for transformations.
NLVM – Transformation Composition/Translations
http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_301_g_3_t_3.html
NLVM – Reflections
http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_297_g_3_t_3.html
NLVM – Rotations
